When you ask, “Where do bobcats live?” you’re exploring one of North America’s most adaptable and widespread wildcats.
Bobcats can be found in a variety of habitats, from dense forests to urban environments.
Their ability to thrive in so many different regions is one of the reasons they’re such a fascinating species.
In this article, we will explore where bobcats live, how they adapt to each environment, and what makes these places ideal for their survival.
So Where Do Bobcats Live?
Forests and Woodlands
Bobcats are most commonly found in forests and woodlands. These environments offer a perfect balance of shelter, food, and space.
Whether it’s the thick forests of the Eastern United States or the towering trees of the Pacific Northwest, bobcats can be spotted living in these lush areas.
These habitats provide abundant prey, like rabbits and squirrels, as well as plenty of places for bobcats to hide from larger predators.
In these forested areas, bobcats find shelter in dense underbrush, fallen logs, and caves. They use the cover of trees and shrubs to stalk prey.
This makes forests one of the most important habitats for bobcats, offering both protection and plentiful food.
Mountains and Rocky Hillsides
Bobcats also live in mountainous regions. From the rugged slopes of the Rocky Mountains to the steep hills of the Appalachians, bobcats can adapt to these varied terrains.
The mountainous habitat offers them rocky outcrops, caves, and crevices, which provide excellent shelter and safety from predators.
These areas are also home to larger prey like deer, which bobcats can hunt. Their agility and stealth make them well-suited for navigating rocky landscapes and tracking their prey.
Bobcats living in mountains are solitary hunters, often covering vast areas in search of food.
Related Article – What Do Bobcats Look Like
Deserts and Arid Regions
Despite their harsh conditions, deserts are also a place where bobcats live. Deserts like the Sonoran and Mojave are home to bobcats, who thrive in the arid heat.
Bobcats in desert habitats typically find shelter in caves, rocky outcroppings, and dense vegetation, where they can hide from the heat and predators.
In these dry environments, bobcats primarily hunt small mammals like rabbits and rodents. They are nocturnal hunters, taking advantage of cooler night temperatures to stalk prey. The desert environment may seem inhospitable, but bobcats are well-adapted to survive here.
Suburban Areas
Interestingly, bobcats have also made their way into urban and suburban areas. As human development increases, bobcats have adapted to these environments, taking refuge in parks, vacant lots, and even along highways.
In cities like Los Angeles, bobcats are spotted in residential areas, where they live in green spaces and hunt rodents.
Bobcats in urban settings are generally nocturnal to avoid human interaction. They have adapted well to urban landscapes, using fences, roofs, and parks as their shelter.
The abundance of food, like rodents and small pets, makes cities and suburbs an ideal environment for bobcats to thrive.
Grasslands and Open Plains
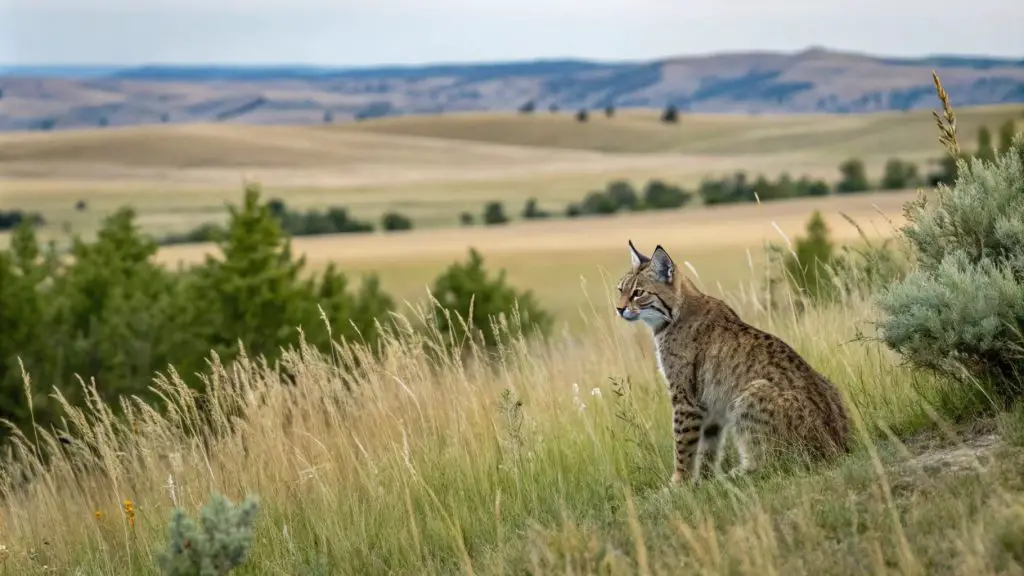

Though less common, bobcats also live in grasslands and open plains. These areas provide wide visibility and open spaces, which are beneficial for hunting.
Bobcats living in grasslands hunt small mammals like rabbits and birds. They rely on the tall grass for cover as they stalk their prey.
While grasslands do not provide as many shelter options as forests, bobcats in these areas adapt by using what is available, such as rocky outcroppings or tall shrubs, for protection and resting spots.
Related Article – Are Bobcats Nocturnal Diurnal or Crepuscular
Wetlands and Swampy Areas
Wetlands and swampy areas also serve as habitats for some bobcats. These regions, rich in food sources like amphibians, small mammals, and fish, offer bobcats an opportunity to thrive.
Wetlands provide bobcats with dense vegetation and hiding spots, as well as an abundance of prey during the warmer months.
Bobcats in these areas hunt in the water and along the banks, preying on frogs, birds, and rodents. While wetlands present challenges such as flooding, bobcats are resourceful and find ways to live and hunt in these unique environments.
Why Bobcats Are Expanding Into Urban Areas
The increase in bobcat sightings in urban areas results from several factors. As human populations grow and natural habitats shrink, bobcats are forced to adapt to the urban environment.
With more green spaces and parks offering cover, bobcats can still find shelter and food, including rodents and small pets.
Bobcats in urban areas have learned to avoid human interaction by being nocturnal. They use fences, vacant lots, and even rooftops to get around, making them highly adaptable.
As they expand into these new territories, bobcats continue to maintain their role as predators, keeping the rodent population in check in many cities.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, bobcats are incredibly versatile creatures that can live in a wide range of habitats.
From dense forests and rugged mountains to urban landscapes and deserts, bobcats have shown their ability to adapt to different environments.
Their hunting skills, stealth, and ability to find shelter have allowed them to survive and thrive in many regions.
Whether you’re exploring the forests of the East or the suburbs of California, there’s a good chance you may find bobcats living right in your backyard—or at least nearby!
Related Article – Are Foxes Nocturnal?
Resources – (for further reading)
Smithsonian’s National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute – Bobcat
National Geographic Kids – Bobcat Animal Profile
National Geographic – Bobcat, facts and information
Brittney , a devoted exotic pet enthusiast, showcases her profound passion for the animals through her role as a veterinary technician. With a strong background in caring for a diverse array of animals, she shares her expertise by crafting engaging articles about exotic pets for our blog.

