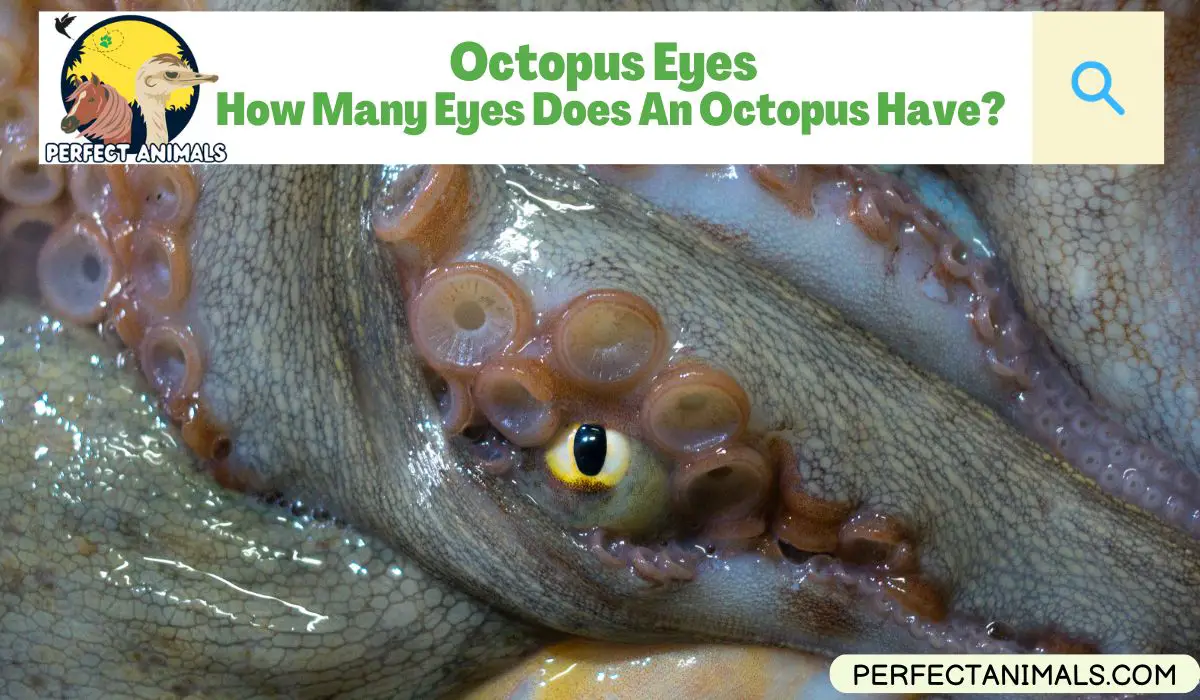
With eight arms covered in suckers and a rounded head, octopuses have an unmistakable appearance, unlike any other sea creature.
Their eyes are also quite unique, containing complex structures that set them apart from human eyes.
In this article, we’ll look at some key facts about octopus eyes—how many they have, whether they have pupils, and how their visual abilities compare to ours.
We’ll discuss what makes their eyes special from an anatomical perspective and why this gives octopuses certain advantages for vision underwater.
By the end, you’ll better understand these fascinating organs and what they can do.
For now, it’s enough to know that octopus eyes are marvels of evolution with capabilities far beyond our own.
Read on to learn more about these wonders of the deep and how octopuses use them to perceive the world around them.
What Color Are Octopus Eyes?
The eyes of octopuses can display a variety of colors, ranging from yellow and brown to green and blue.
The specific color is determined by pigments within the eye.
Octopuses have a single layer of pigment cells, known as iridophores and leucophores, that reflect light and produce color.
Iridophores create iridescent blues and greens, while leucophores generate yellows and browns.
Different octopus species have different predominant eye colors that blend with their habitats.
Shallow-water octopuses that live around coral reefs tend to have striking blue eyes.
Deep sea octopuses have evolved eyes that match the dark environment.
For example, the dumbo octopus has cloudy grayish-blue eyes that blend into the dark ocean depths.
The common octopus usually has yellowish eyes, while the giant Pacific octopus often exhibits reddish-brown eyes.
Related Article – Orcas Eyes | Amazing Facts You Never Knew
How Many Eyes Does An Octopus Have?
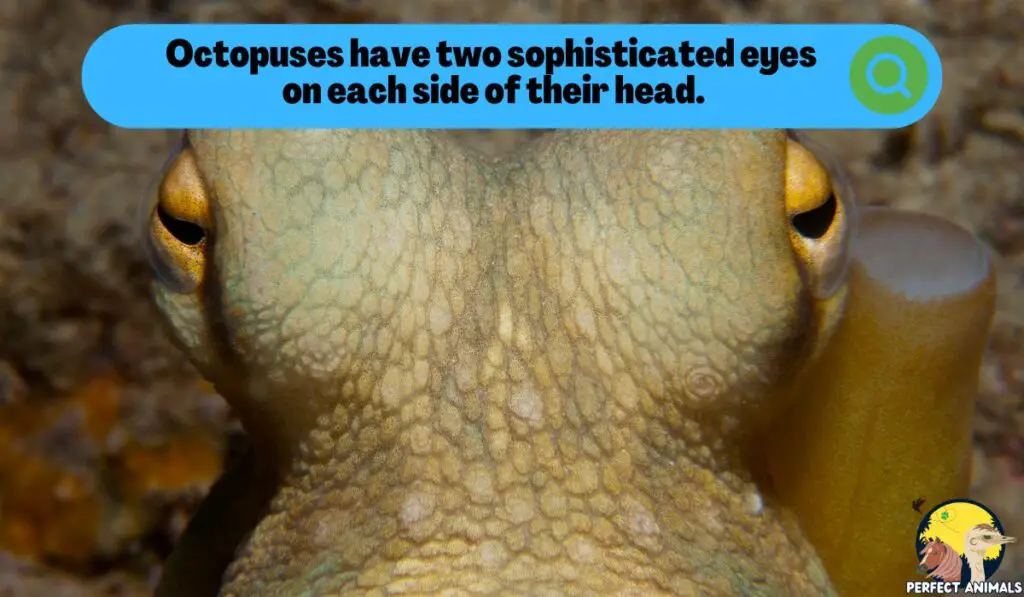
Octopuses have two large, complex eyes located on either side of their head. These eyes are quite sizable, typically about the size of a tennis ball in common species like the common octopus.
Giant Pacific octopuses have slightly smaller, more oval-shaped eyes.
But relative to their body size, octopus eyes are generally quite large overall.
Having two eyes gives octopuses the advantage of stereoscopic vision.
Like humans, their dual vision allows them to perceive depth and distance. Each eye can focus independently, providing sharp vision.
The placement of their eyes on the sides of the head also gives octopuses an extra-wide visual field.
They can see objects and motion approaching from nearly any direction.
This gives them better situational awareness to spot both prey and potential predators lurking in their peripheral vision.
Related Article – Can Sharks See in the Dark?
Do Octopus Eyes Have Pupils?
Yes, octopuses do have pupils in their eyes.
The octopus’s pupil is circular and black when in darkness. But when exposed to bright light, it constricts into a narrow horizontal slit.
This automatic response controls how much light enters the eye.
Surrounding the pupil is a structure called the iris.
But unlike the human iris, the octopus’s iris lies on top of the lens rather than behind it.
The iris contains pigments that determine eye color and also help restrict light levels.
One unique aspect of octopus pupils is their dumbbell shape. This causes a chromatic aberration effect, scattering white light into an array of colors.
When an octopus looks downward, the U-shaped wrap of its pupil around the eyeball creates a similar color-separating effect.
Octopuses also have an involuntary reflex that keeps their slit-like pupils horizontally aligned at all times.
This orientation is controlled by the statocyst, an organ below the brain that monitors balance and head orientation.
You May Also Like – Do Fish Blink? Fact or Fiction?
What Colors Can An Octopus See?
Octopuses have only one type of light receptor cell (photoreceptor) in their eyes, which means they can see only in black and white – no color vision.
However, research shows they are able to distinguish some colors like blue and yellow. Their vision is limited compared to humans who see the full spectrum.
One theory for how octopuses can see hints of color is by changing the depth of their eyeball.
Adjusting the eyeball depth may allow different wavelengths of light to focus individually on the retina, providing a sense of color.
Octopuses can also detect polarized light, as we explained in the previous section about their pupils.
This polarized light sensitivity aids navigation and orientation underwater. It may also enhance contrast when hunting prey.
So while octopus color vision is quite limited compared to humans, some hues like blue and yellow are perceptible.
Their ability to control eyeball depth and perceive polarized light seem to provide an alternate visual advantage in the marine environment.
More research is still needed to fully understand the nuances of octopus color vision.
You May Also Like – Do Barracudas Eat Fish Eggs?
Final Thoughts
The eyes of octopuses are truly marvels of evolution that are uniquely adapted to the challenges of underwater vision.
Their placement, size, pupil shape, and ability to detect polarized light all provide advantages to octopuses that humans lack.
While their color vision is limited compared to the human eye, the octopus eye excels at discerning contrast, movement, and light levels to capture prey and avoid danger in the ocean depths.
With their shiftiness and strangeness, octopus eyes remind us how diverse vision can be across life on Earth.
And who knows what discoveries remain about how these cephalopods perceive their environment?
Their eyes surely still hold many secrets left to unravel.
FAQs
How many eyes does an octopus have?
Octopuses have two large, complex eyes.
Can an octopus see in the dark?
Yes, octopuses can see well in dim light and darkness thanks to their large pupil size and light-sensitive cells.
How do octopuses change colors if they are colorblind?
While not fully colorblind, octopuses have limited color vision. Their color-changing ability is an involuntary response based on things like mood, not reliant on seeing color.
What advantage do octopus eyes have over human eyes?
Advantages include a wider field of view, the ability to independently move/focus eyes, control over pupil shape/size, and detection of polarized light. Their eyes are optimized for the marine environment.
Resources – (for further reading)
Frontiers – The Eye of the Common Octopus (Octopus vulgaris)
Smithsonian Ocean – Octopus Eyes | Smithsonian Ocean
National Institutes of Health (.gov) – The Eye of the Common Octopus (Octopus vulgaris) – PMC

Sofi has worked as an educator at the Miami Seaquarium, where she conducted educational programs about marine life. In her free time, she contributes to our platform, sharing her passion for marine ecosystems and their conservation.